| You are not Logged In! |
Difference between revisions of "Public:KiCad"
imported>Amalia |
|||
| (130 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ''See [[PCB Design]] for design basics & guidelines. See [[Public:GitHub]] for setting up the files you're going to work with.'' | ||
| − | + | [https://www.kicad.org/ KiCad] is the e-cad (electrical computer aided design) program we use exclusively since 2018. It is an open-source project and is constantly improving and growing in capabilities. It has many advantages for a distributed long-term student project including that it is free/open-source, has human readable files, and is scriptable with python. On this page you will find info on getting your KiCad Install Setup for use on Illini Solar Car. | |
| − | + | If you have any trouble with this set-up you can get help on {{SlackLink|elec-cad}} or speak to other electrical team members. | |
| − | { | + | {{RemarksBox Info|Title=We use KiCad v8|Text=We are currently using KiCad v8. Major versions of KiCad are not cross-compatible. Make sure you use a KiCad v8 production release. Nightly Releases are also not compatible with production releases.}} |
| + | {{RemarksBox Warn|Title=Images may Differ|Text=Minor versions of KiCad v8 have had many cosmetic updates, the images below may look a bit different than what you see.}} | ||
| − | { | + | {{RemarksBox |
| + | | bordercolor = #F5C6CB | ||
| + | | backgroundcolor = #F8D7DA | ||
| + | | iconfile = Error Icon.png | ||
| + | | width = 100% | ||
| + | | Title = Use the Template for New Designs | ||
| + | | Text = You must start your projects from the KiCad v8 template or they will not be accepted! This can be found in the Dev folder of our PCB repo. If you have started without the template you should create a new project from the template and copy your board into that (Note: in KiCad v8 this is a simple ctrl+c, ctrl+v). You can ask for help with this on {{SlackLink|elec-cad}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | [ | + | == First Time Setup == |
| + | A video tutorial for downloading and setting up [[GitHub]] as well as cloning the PCB repository can be found in [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6VV7DvNGEA8&list=PLYWKqdG09eYLCqh8V8gjJpYXOJ60yJ5xG&index=1 the first video of Rahul's KiCad tutorials playlist]. The video goes over KiCad v5, but the installation process is very similar to v8. | ||
| − | { | + | === Install and Run === |
| + | # [https://www.kicad.org/download/ Download the latest '''8.x.x''' version] of KiCad for your operating system | ||
| + | #* Some OS's have special instuctions - follow them. | ||
| + | #** Note that KiCad has historically had stability issues on OSX / MacOS. If you have access to Windows or Linux those are recommended. | ||
| + | #* KiCad is available on many Linux package managers - make sure you do not get the nightly version. | ||
| + | #* Otherwise KiCad installs like any other program | ||
| + | # As you go through the install wizard you can use the default options | ||
| + | #* You can optionally deselect the ''Help article'' languages you don't want, as well as deselect the ''Demonstration projects'', since we have completed projects for you to look at already | ||
| + | # Enjoy, and check this wiki as well as the [https://docs.kicad.org/ KiCad help resources] before asking about issues on {{SlackLink|elec-cad}} | ||
| − | '' | + | === Library Setup === |
| + | ''Note: This applies to KiCad v6, v7, and v8 projects on GitHub since'' {{GithubPRLink|repo=isc-hw-libs|number=84}}.''This should cover most projects, and all new projects. But if you need to view older projects please update them following the instructions at [[Viewing KiCad v5 Projects]]'' | ||
| − | + | Our libraries, as well as KiCad's own schematic symbol libraries, our libraries are now back to their own repo. Make sure you've followed the [[GitHub]] directions in order to get those libraries on your machine. They are in the the seperate [https://github.com/IlliniSolarCar/isc-hw-libs/ isc-hw-libs] repo. If you first open a schematic in KiCad, without setting this up, you'll probably see a lot of question marks (?) all around the schematic. To fix this follow the below instructions. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | To setup the Libraries in General we need to let KiCad know where they are! To prevent our set-up from Interfering with your outside usage of KiCad we use ISC specific Environment Variables. | |
| + | # Open KiCad. Start these Instructions from the home screen | ||
| + | # Click on ''Preferences --> Configure Paths...'' | ||
| + | # Add a new path (press "Add") with the name <code>ISC_SYMBOL_DIR</code> and insert the path to the isc-hw-libs repo: <code>PathOnYourComputer\isc-hw-libs</code> | ||
| + | [[File:KiCad Libs Config.png|none|frame|Your Environment Variable should look like this]]This should be all you need! Our libraries are now managed using project specific libraries specified by the library tables in the project (provided with the template project) | ||
| − | + | === Starting a Project === | |
| − | + | # Create a branch for your project in the PCB Repo (See [[GitHub/PCB]] for specific guidelines) <code>git checkout -b <branch></code> | |
| + | #* If you need to make new symbols or footprints see [[Adding Symbols %26 Footprints to KiCad]] you also need to create a branch in the [https://github.com/IlliniSolarCar/isc-hw-libs/ isc-hw-libs] repo. If you are unsure, you can always do this later when the need arises. (See [[GitHub/Libraries]] for more info) | ||
| + | # Copy the latest template from the Dev Folder (make sure you <code>git checkout master</code> and <code>git pull</code>first) <code>PathOnYourComputer\PCB/Dev/Template_v0.0</code> to the location where your project will live | ||
| + | # Rename your project following the naming conventions - you will need to rename the folder and every named file manually. | ||
| + | #* Do not rename the <code>.kicad_wks</code> file or others files not named for the template - otherwise your settings and/or libraries may not be set-up right | ||
| + | # Make an initial commit to the PCB Repo to create your branch on Github. (Use <code>git push --set-upstream origin <branch> </code> for the first push) | ||
| − | + | Now you are good to go working on your project! Make sure to follow the [[Schematic Conventions]] and [[Layout Standards]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | == Making a PCB Revision == |
| + | Many times you will be making only small revisions to PCBs so you will branch off the previous project version. I.e. you are making PDS Control v4.1, you will likely copy the files from PDS Control v4.0 into a new folder. You will need to rename the files to the newest version and delete and [[Bay Area Circuits|gerbers]], backup files, or [[Adding a BOM to PartsBox|bom files]]. | ||
| − | + | Additionally you should replace the <code>fp-lib-table</code> and <code>sym-lib-table</code> and <code>Title_Block.kicad_wks</code> files with those present in the PCB repo in <code>PathOnYourComputer\PCB/Dev/Template_v0.0</code> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''An in-depth guide on the steps to take is provided in [https://youtu.be/bkXfB56ZAzU this video] by [[User:Lukeag3|Luke]]''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Viewing Old Projects == |
| − | + | Some projects you may want to view, such as previous board version, may be made with an older software. To view them you'll need to do a bit of work using the instructions linked below: | |
| − | [[ | + | * For KiCad v4 Projects - follow the instructions at [[Upgrading a project from KiCad 4 to KiCad 5]] |
| − | * | + | * For KiCad v5 Projects - follow the instructions at [[Viewing KiCad v5 Projects]] |
| − | + | * For KiCad v6 Projects - follow the instructions at [[Viewing KiCad v6 Projects]] | |
| − | * | + | * For KiCad v7 Projects - follow the instructions at [[Viewing KiCad v7 Projects]] |
| − | + | * For Diptrace files you will need to install Diptrace to view. See [[Electrical Software Instructions]] for info on activation and install. | |
| − | + | * For KiCad Projects without library tables (we originally used Global Libraries) | |
| − | + | ** You should be able to just copy the tables from the template - but if you have issues you can follow the old library set-up (used before {{GithubPRLink|repo=PCB|number=62}}) | |
| − | + | {{Collapsible Box|title=Old Library Set-up|content='''General''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# Click on ''Preferences'' --> ''Configure Paths...'' | # Click on ''Preferences'' --> ''Configure Paths...'' | ||
| − | # Change KICAD_SYMBOL_DIR (click on it and then | + | # Change <code>KICAD_SYMBOL_DIR</code> (click on it and then "Edit") to the path of the Libraries folder |
| − | + | #* The Libraries folder should be <code><ISC folder>\isc-hw-libs</code> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''Schematic Symbols''' | ||
''Assumes you have eeschema open'' | ''Assumes you have eeschema open'' | ||
# ''If in Project window, otherwise go to next step.'' Click on ''Tools'' --> ''Edit Schematic Symbols...'' | # ''If in Project window, otherwise go to next step.'' Click on ''Tools'' --> ''Edit Schematic Symbols...'' | ||
| − | + | #* If this is the first time you've run eeschema (or possibly after an update), it will ask you to "Configure Global Symbol Library Table". Stick with the default and click ''Ok'' | |
| − | + | #* If you get a whole bunch of errors, then hold the ESC key until they're done. At least you know you're in the right place to fix those! | |
# ''Skip #1 to go here if you have a schematic open.'' Click on ''Preferences'' --> ''Manage Symbol Libraries...'' | # ''Skip #1 to go here if you have a schematic open.'' Click on ''Preferences'' --> ''Manage Symbol Libraries...'' | ||
| − | + | #* Make sure you are on the Global Libraries tab of the popup box | |
# Select all (ctrl+A or cmd+A) the libraries that are there by default and remove them | # Select all (ctrl+A or cmd+A) the libraries that are there by default and remove them | ||
| − | # Then click on ''Browse Libraries...'' | + | # Then click on ''Browse Libraries...'' --> navigate to the folder called '''schematic''' in the isc-hw-libs repo --> select all --> Click <nowiki>''</nowiki>Open<nowiki>''</nowiki> |
| − | + | #* These are the custom ones we've made for solar car parts. | |
| − | + | #* Make sure you add these first; we override some of the default library symbols | |
| − | # '''AGAIN''' click ''Browse Libraries...'' | + | # '''AGAIN''' click ''Browse Libraries...'' --> navigate to the folder called '''schematic_kicad''' in the Libraries folder --> select all --> Click ''Open'' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''Layout Footprints''' | ||
''Assumes you have Pcbnew open'' | ''Assumes you have Pcbnew open'' | ||
# Click on ''Preferences'' --> ''Manage Footprint Libraries...'' | # Click on ''Preferences'' --> ''Manage Footprint Libraries...'' | ||
| − | + | #* Make sure you are on the Global Libraries tab of the popup box | |
# Click ''Browse Libraries...'' | # Click ''Browse Libraries...'' | ||
| − | # Navigate to the | + | # Navigate to the isc-hw-libs repo |
| − | # Inside the | + | # Inside the isc-hw-libs repo is a folder called layout.pretty |
| − | + | #* KiCad uses the .pretty extension on folder names to delineate footprint libraries | |
# Select the layout.pretty folder and click ''OK'' | # Select the layout.pretty folder and click ''OK'' | ||
| − | # In the list of libraries (probably at the bottom) you should now see one called | + | # In the list of libraries (probably at the bottom) you should now see one called "layout" |
| − | # Click ''OK'' again to exit the library manager | + | # Click ''OK'' again to exit the library manager|autocollapse=true|width=100%}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ( | + | == Bill of Materials == |
| + | The Bill of Materials (BOM) is the list of parts you need in order to fully assemble the board. Since all this info is in KiCad, we just have to get it out in a format that is useful for what we are doing with it! | ||
| − | == | + | Before you begin, you need to make sure that all of your parts have the required information as specified in the [[Schematic Conventions]]. |
| + | {{RemarksBox Error|Title=Our BOM Methods need improvement|Text=Note that we don't have a great BOM system as of now. Currently, there is a lot of manual work to make sure to get it right. If you want to work on this, you can make this better with Python Scripts/Plugins and/or [[GitHub Actions]]!}} | ||
| + | The ''Tools -> Edit Symbol Fields'' table can act as a BOM Previewer within KiCad to view all of your parts and their info. You can also mass edit things (such as applying part numbers to a bunch of the same part) | ||
| − | + | See the [[Adding a BOM to PartsBox]] for our current workflow and [[KiCad/BOM]] page for info on how to export the BOM for different usages! | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Export for Manufacturing == | |
| − | + | To manufacture your files you simply need to export the [https://bayareacircuits.com/are-you-providing-your-pcb-manufacturer-with-the-correct-files/ needed files]. That is, [[wikipedia:Gerber_format|the Gerber X2 Files]] for each relevant layer and the drill file for the board outline and holes (such as mounting). You will do this using KiCad Plot functionality. | |
| − | + | # You can follow [https://uofi.app.box.com/file/1805212146799 this] to export the files for your board. | |
| − | * | + | #* Make sure the drill file is exported in '''millimeters''', not mils or inches. Otherwise the Bay Area Circuits DFM will round and possible fail your board due to rounding. |
| − | + | # Compress all of the files into a .zip file. This .zip is what will be sent to the manufacturer and what goes on Git. Do not upload the individual files. This .zip should be inside your project folder | |
| − | + | # Once you have this .zip you can run the DFM report to make sure that passes | |
| − | + | # When the Board Run is ready the DFM report and zip file will be sent in. | |
| − | + | # For assembly you will also need the Bill of Materials (above) in [[Partsbox]], [[Adding a BOM to PartsBox]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Plugins == | |
| + | KiCad makes it really easy to integrate 3rd party plugins in KiCad. A plugin is essentially just a python script that you can run from inside KiCad so it has access to what you are currently working on. You can find KiCad plugins online from many sources to do all sorts of things. Additionally, we may also develop some of our own. | ||
| − | + | Installing Plugins is easy, just place the plugin files in their own folder in the KiCad Plugins folder. This differs by OS: | |
| + | * Windows: <code>%APPDATA%\kicad\scripting\plugins</code> | ||
| + | * Linux: <code>/usr/share/kicad/scripting/plugins/</code> | ||
| + | * Mac: <code>~/Library/Application Support/kicad/scripting/plugins</code> | ||
| + | If you have KiCad open you can add the Plugin by going to <code>Tools -> External Plugins -> Refresh</code> although some may need a full restart of KiCad | ||
| − | ///// | + | Some useful Plugins, we recommend that everyone install HTML BOM - install others as needed: |
| + | * [https://github.com/openscopeproject/InteractiveHtmlBom Interactive HTML BOM], useful for helping you while building a board. See [[KiCad/BOM]] for more info | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/easyw/RF-tools-KiCAD RF Tools]: Includes several tools, not only useful for RF, including Curved Traces, Track Length Matching, Via Fencing | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/NilujePerchut/kicad_scripts/tree/master/teardrops Teardrops] : makes teardrops into vias and/or pads which increases the inferface between the trace and the via/pad. Most useful to reduce mechanical/thermal strain and thus prevent cracking traces | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/jsreynaud/kicad-action-scripts Via Stitching and Circular Zones]: Stitch together copper areas with vias more easily and create round copper zones | ||
| − | + | == Useful Links == | |
| − | + | [https://shawnhymel.com/portfolio/video-series-introduction-to-kicad/ Shawn Hymel's Tutorials] - videos for every step of PCB design and manufacture | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [https://www.kicad.org/help/ KiCad's own website] - videos, example PCBs, and textual tutorials can be found under "learning resources" | |
| − | + | [https://www.build-electronic-circuits.com/kicad-tutorial/ "Make Your First Board"] - great tutorial for visual learners | |
| − | + | [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLYWKqdG09eYLCqh8V8gjJpYXOJ60yJ5xG Rahul's tutorial videos] - Created during Electrical Onboarding 2020, great guide for getting started with the team | |
| + | {{PCB Design Navbox|collapsed=}} | ||
| + | [[Category:KiCad]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:59, 16 March 2025
See PCB Design for design basics & guidelines. See Public:GitHub for setting up the files you're going to work with.
KiCad is the e-cad (electrical computer aided design) program we use exclusively since 2018. It is an open-source project and is constantly improving and growing in capabilities. It has many advantages for a distributed long-term student project including that it is free/open-source, has human readable files, and is scriptable with python. On this page you will find info on getting your KiCad Install Setup for use on Illini Solar Car.
If you have any trouble with this set-up you can get help on ![]() elec-cad or speak to other electrical team members.
elec-cad or speak to other electrical team members.
| Images may Differ | |
| Minor versions of KiCad v8 have had many cosmetic updates, the images below may look a bit different than what you see. | |
| Use the Template for New Designs | |
| You must start your projects from the KiCad v8 template or they will not be accepted! This can be found in the Dev folder of our PCB repo. If you have started without the template you should create a new project from the template and copy your board into that (Note: in KiCad v8 this is a simple ctrl+c, ctrl+v). You can ask for help with this on | |
First Time Setup
A video tutorial for downloading and setting up GitHub as well as cloning the PCB repository can be found in the first video of Rahul's KiCad tutorials playlist. The video goes over KiCad v5, but the installation process is very similar to v8.
Install and Run
- Download the latest 8.x.x version of KiCad for your operating system
- Some OS's have special instuctions - follow them.
- Note that KiCad has historically had stability issues on OSX / MacOS. If you have access to Windows or Linux those are recommended.
- KiCad is available on many Linux package managers - make sure you do not get the nightly version.
- Otherwise KiCad installs like any other program
- Some OS's have special instuctions - follow them.
- As you go through the install wizard you can use the default options
- You can optionally deselect the Help article languages you don't want, as well as deselect the Demonstration projects, since we have completed projects for you to look at already
- Enjoy, and check this wiki as well as the KiCad help resources before asking about issues on
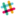 elec-cad
elec-cad
Library Setup
Note: This applies to KiCad v6, v7, and v8 projects on GitHub since ![]() isc-hw-libs#84.This should cover most projects, and all new projects. But if you need to view older projects please update them following the instructions at Viewing KiCad v5 Projects
isc-hw-libs#84.This should cover most projects, and all new projects. But if you need to view older projects please update them following the instructions at Viewing KiCad v5 Projects
Our libraries, as well as KiCad's own schematic symbol libraries, our libraries are now back to their own repo. Make sure you've followed the GitHub directions in order to get those libraries on your machine. They are in the the seperate isc-hw-libs repo. If you first open a schematic in KiCad, without setting this up, you'll probably see a lot of question marks (?) all around the schematic. To fix this follow the below instructions.
To setup the Libraries in General we need to let KiCad know where they are! To prevent our set-up from Interfering with your outside usage of KiCad we use ISC specific Environment Variables.
- Open KiCad. Start these Instructions from the home screen
- Click on Preferences --> Configure Paths...
- Add a new path (press "Add") with the name
ISC_SYMBOL_DIRand insert the path to the isc-hw-libs repo:PathOnYourComputer\isc-hw-libs
This should be all you need! Our libraries are now managed using project specific libraries specified by the library tables in the project (provided with the template project)
Starting a Project
- Create a branch for your project in the PCB Repo (See GitHub/PCB for specific guidelines)
git checkout -b <branch>- If you need to make new symbols or footprints see Adding Symbols & Footprints to KiCad you also need to create a branch in the isc-hw-libs repo. If you are unsure, you can always do this later when the need arises. (See GitHub/Libraries for more info)
- Copy the latest template from the Dev Folder (make sure you
git checkout masterandgit pullfirst)PathOnYourComputer\PCB/Dev/Template_v0.0to the location where your project will live - Rename your project following the naming conventions - you will need to rename the folder and every named file manually.
- Do not rename the
.kicad_wksfile or others files not named for the template - otherwise your settings and/or libraries may not be set-up right
- Do not rename the
- Make an initial commit to the PCB Repo to create your branch on Github. (Use
git push --set-upstream origin <branch>for the first push)
Now you are good to go working on your project! Make sure to follow the Schematic Conventions and Layout Standards.
Making a PCB Revision
Many times you will be making only small revisions to PCBs so you will branch off the previous project version. I.e. you are making PDS Control v4.1, you will likely copy the files from PDS Control v4.0 into a new folder. You will need to rename the files to the newest version and delete and gerbers, backup files, or bom files.
Additionally you should replace the fp-lib-table and sym-lib-table and Title_Block.kicad_wks files with those present in the PCB repo in PathOnYourComputer\PCB/Dev/Template_v0.0
An in-depth guide on the steps to take is provided in this video by Luke
Viewing Old Projects
Some projects you may want to view, such as previous board version, may be made with an older software. To view them you'll need to do a bit of work using the instructions linked below:
- For KiCad v4 Projects - follow the instructions at Upgrading a project from KiCad 4 to KiCad 5
- For KiCad v5 Projects - follow the instructions at Viewing KiCad v5 Projects
- For KiCad v6 Projects - follow the instructions at Viewing KiCad v6 Projects
- For KiCad v7 Projects - follow the instructions at Viewing KiCad v7 Projects
- For Diptrace files you will need to install Diptrace to view. See Electrical Software Instructions for info on activation and install.
- For KiCad Projects without library tables (we originally used Global Libraries)
- You should be able to just copy the tables from the template - but if you have issues you can follow the old library set-up (used before
 PCB#62)
PCB#62)
- You should be able to just copy the tables from the template - but if you have issues you can follow the old library set-up (used before
General
- Click on Preferences --> Configure Paths...
- Change
KICAD_SYMBOL_DIR(click on it and then "Edit") to the path of the Libraries folder- The Libraries folder should be
<ISC folder>\isc-hw-libs
- The Libraries folder should be
Schematic Symbols Assumes you have eeschema open
- If in Project window, otherwise go to next step. Click on Tools --> Edit Schematic Symbols...
- If this is the first time you've run eeschema (or possibly after an update), it will ask you to "Configure Global Symbol Library Table". Stick with the default and click Ok
- If you get a whole bunch of errors, then hold the ESC key until they're done. At least you know you're in the right place to fix those!
- Skip #1 to go here if you have a schematic open. Click on Preferences --> Manage Symbol Libraries...
- Make sure you are on the Global Libraries tab of the popup box
- Select all (ctrl+A or cmd+A) the libraries that are there by default and remove them
- Then click on Browse Libraries... --> navigate to the folder called schematic in the isc-hw-libs repo --> select all --> Click ''Open''
- These are the custom ones we've made for solar car parts.
- Make sure you add these first; we override some of the default library symbols
- AGAIN click Browse Libraries... --> navigate to the folder called schematic_kicad in the Libraries folder --> select all --> Click Open
Layout Footprints Assumes you have Pcbnew open
- Click on Preferences --> Manage Footprint Libraries...
- Make sure you are on the Global Libraries tab of the popup box
- Click Browse Libraries...
- Navigate to the isc-hw-libs repo
- Inside the isc-hw-libs repo is a folder called layout.pretty
- KiCad uses the .pretty extension on folder names to delineate footprint libraries
- Select the layout.pretty folder and click OK
- In the list of libraries (probably at the bottom) you should now see one called "layout"
- Click OK again to exit the library manager
Bill of Materials
The Bill of Materials (BOM) is the list of parts you need in order to fully assemble the board. Since all this info is in KiCad, we just have to get it out in a format that is useful for what we are doing with it!
Before you begin, you need to make sure that all of your parts have the required information as specified in the Schematic Conventions.
| Our BOM Methods need improvement | |
| Note that we don't have a great BOM system as of now. Currently, there is a lot of manual work to make sure to get it right. If you want to work on this, you can make this better with Python Scripts/Plugins and/or GitHub Actions! | |
The Tools -> Edit Symbol Fields table can act as a BOM Previewer within KiCad to view all of your parts and their info. You can also mass edit things (such as applying part numbers to a bunch of the same part)
See the Adding a BOM to PartsBox for our current workflow and KiCad/BOM page for info on how to export the BOM for different usages!
Export for Manufacturing
To manufacture your files you simply need to export the needed files. That is, the Gerber X2 Files for each relevant layer and the drill file for the board outline and holes (such as mounting). You will do this using KiCad Plot functionality.
- You can follow this to export the files for your board.
- Make sure the drill file is exported in millimeters, not mils or inches. Otherwise the Bay Area Circuits DFM will round and possible fail your board due to rounding.
- Compress all of the files into a .zip file. This .zip is what will be sent to the manufacturer and what goes on Git. Do not upload the individual files. This .zip should be inside your project folder
- Once you have this .zip you can run the DFM report to make sure that passes
- When the Board Run is ready the DFM report and zip file will be sent in.
- For assembly you will also need the Bill of Materials (above) in Partsbox, Adding a BOM to PartsBox
Plugins
KiCad makes it really easy to integrate 3rd party plugins in KiCad. A plugin is essentially just a python script that you can run from inside KiCad so it has access to what you are currently working on. You can find KiCad plugins online from many sources to do all sorts of things. Additionally, we may also develop some of our own.
Installing Plugins is easy, just place the plugin files in their own folder in the KiCad Plugins folder. This differs by OS:
- Windows:
%APPDATA%\kicad\scripting\plugins - Linux:
/usr/share/kicad/scripting/plugins/ - Mac:
~/Library/Application Support/kicad/scripting/plugins
If you have KiCad open you can add the Plugin by going to Tools -> External Plugins -> Refresh although some may need a full restart of KiCad
Some useful Plugins, we recommend that everyone install HTML BOM - install others as needed:
- Interactive HTML BOM, useful for helping you while building a board. See KiCad/BOM for more info
- RF Tools: Includes several tools, not only useful for RF, including Curved Traces, Track Length Matching, Via Fencing
- Teardrops : makes teardrops into vias and/or pads which increases the inferface between the trace and the via/pad. Most useful to reduce mechanical/thermal strain and thus prevent cracking traces
- Via Stitching and Circular Zones: Stitch together copper areas with vias more easily and create round copper zones
Useful Links
Shawn Hymel's Tutorials - videos for every step of PCB design and manufacture
KiCad's own website - videos, example PCBs, and textual tutorials can be found under "learning resources"
"Make Your First Board" - great tutorial for visual learners
Rahul's tutorial videos - Created during Electrical Onboarding 2020, great guide for getting started with the team
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||