| You are not Logged In! |
Difference between revisions of "Public:GitHub"
(Link to new PCB page) |
|||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
and [[GitHub/isc-hw-libs]] | and [[GitHub/isc-hw-libs]] | ||
</tab> | </tab> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<tab name="FW">== FW (Firmware)== | <tab name="FW">== FW (Firmware)== | ||
| − | + | See [[GitHub/b-fw]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</tab> | </tab> | ||
<tab name="Strategy and Telemetry"> | <tab name="Strategy and Telemetry"> | ||
Revision as of 22:57, 22 September 2020
| This Page is a Work In Progress | |
| Moving to subpages, getting rid of tabs, adding info for the other Repos. This page will turn into generally using github - Jonathan | |
| Note | |
| This page is about the set-up and workflow we use on Github. Other pages are used for how git is used with certain software such as KiCad or MCUXpresso. Additionally, it does not include info about github management, teams, and projects as used by Illini Solar Car, which is at GitHub Projects | |
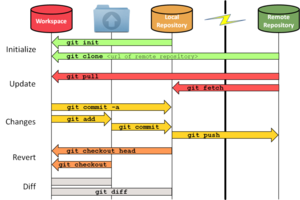
Illini Solar Car has several git repositories within our organization on GitHub. You must talk with an Electrical Lead or Strategy & Telemetry Lead so they can give you access to our private repositories. In general, many people use git via the command line. We use it almost exclusively, and you should learn it in order to git (haha) on the same page as everyone else. On most Linux distros this is included in command line. On Mac and Windows you can download git. When "Adjusting your PATH environment," I recommend selecting "Use Git from Git Bash" and not using git in the Windows Command Prompt. When "Configuring the line ending conversions" please use the settings recommended for your operating system unless you know what you are doing.
If you're new to Github they're many resources on the internet to learn more about it. Watching some youtube videos on the basics and trying it out by creating your own repository is a great way to get started.
General Guidelines
- Make your commit messages useful
- Pull often!
- Commit often (but not too often)
- If you aren't sure what you are doing ask for help!
- If you think you broke something talk to someone right away!
- It essentially always fixable but we want to do so quickly so others don't run into problems
Info on how to use git by group:
PCB
See GitHub/PCB and GitHub/isc-hw-libs
FW (Firmware)
See GitHub/b-fw
The strategy and telemetry group currently has 3 repositories: Telemetry, data-analysis, and Athena-v2.
Information about these repositories and their setups can be found in the README.md files in each repository.
clone the repository using git clone --recursive <repo> and git clone <repo> for the other two.
The --recursive option looks for submodules in the repo and clones them into the correct directory. If this option was omitted during the initial clone, run the command git submodule update --init to find any un-cloned submodules and clone them. This only applies to the Telemetry repo that contains the CAN submodule with the CAN messages for the car.
About Repos
The Telemetry repo primarily holds the code for the telemetry application, the app that allows us to view and analyze car data in real time to diagnose issues and make informed decisions.
The data-analysis repo hold code used to analyze datalogger race data after the races to better understand the car and its performance.
The Athena-v2 repo has code that is currently an in-progress project currently delayed until more man and woman power is available to code. The project is a car simulation and optimizer to determine optimal strategy decisions in a calculated and methodical way.
Workflow
The workflow of branches and commits should be similar to how the FW repo works. All work should be done in separate branches if multiple people are working on one feature, they should each have their own branches and merge them together when possible. Branches should not be merged into master until they are known to work without breaking the system.
To merge a branch in to master a pull request should be made and at least two reviewers should be requested. Once these reviewers have approved the pull request can be merged into master.
If changes need to be made quickly and shared and there is not time to follow the review process (for example during a race) a separate branch of master should be made for this. The changes should then be reviewed and cleaned when there is time and then the standard merging procedure should be followed to pull the changes into master.
Tutorials
Git is a super useful tool that is becoming ubiquitous with CS / ECE and more engineering fields. It is used for all sorts of things (not just code) . Version control is incredibly powerful, but because of that it can be hard to learn. Below are some recommended tutorials. Of course, as git was made for code, there is tons of info on the internet. Being good with git will be very helpful within jobs and academics.